MDL Language#
The MDL language in Omniverse is used for creating and describing physically-based materials. It provides a flexible and powerful way to define material properties, such as appearance, texture mapping, and light interaction. With MDL, users can create complex materials with realistic details, including effects like reflections, refractions, and surface patterns. These materials can be applied to 3D objects and used in rendering scenes to achieve high-quality visual results. MDL in Omniverse USD Composer enables artists and designers to create and manipulate materials in a visually intuitive manner, while also providing the flexibility to fine-tune material properties through code-based scripting if desired.
You can read more about the MDL language in the following.
We are constantly adding features and support of the MDL language in Omniverse.
MDL Annotations#
Note
New annotation support for Kit versions 105.0.1 and higher
- Nested Groups
anno::in_group( string group, string subgroup, string subsubgroup, boolcollapsed=false)
- UI Order
anno::ui_order( int order )
- Hidden
anno::hidden()
- Descriptions as popup tooltip
anno::description( string description )
- Enum Display
Default strings are displayed correctly in the UI.
Note
New annotation support for Kit versions 106.0.0 and higher
Struct Unrolling
anno::node_output_port_default( node port value )
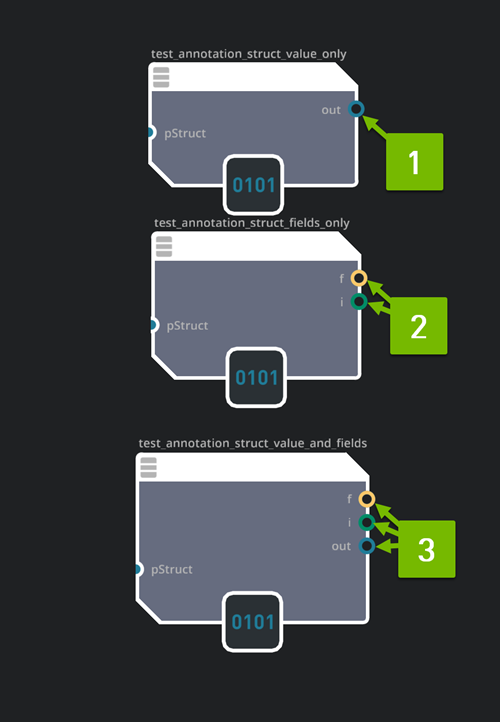
Material Graph nodes support multiple outputs from MDL Functions. MDL Material Graph nodes can use the new MDL 1.8 annotation node_output_port_default and node_port_mode to control how single value struct returns from MDL function integrate with multiple output ports in the Material Editor.
When the annotations are applied to a compound return type of a MDL function or user-defined struct, the Material Editor can output either:
The single value of the return as an output port called out.
Each field of the compound is returned as an output port called by its field name.
Both the compound single value of the return as an output port called out and each field of the compound is returned as an output port called by its field name.
For more information, please refer to MDL Specification 1.10, page 98
Example MDL code for struct unrolling
mdl 1.8;
import ::anno::*;
export struct TestStruct
{
int i = 1;
float f = 0.2;
};
export TestStruct
[[
anno::node_output_port_default(anno::node_port_value_only)
]]
test_annotation_struct_value_and_fields
(
TestStruct pStruct = TestStruct()
)
{
return pStruct;
}
export TestStruct
[[
anno::node_output_port_default(anno::node_port_fields_only)
]]
test_annotation_struct_fields_only
(
TestStruct pStruct = TestStruct()
)
{
return pStruct;
}
export TestStruct
[[
anno::node_output_port_default(anno::node_port_value_and_fields)
]]
test_annotation_struct_value_only
(
TestStruct pStruct = TestStruct()
)
{
return pStruct;
}
The image below shows the how this will appear in the material graph.