Scatter Examples
The goal of these examples are to provide common use cases for scattering in Omniverse Replicator.
Below are a few demonstrations of scatter applied within a scene using Replicator APIs.
Learning Objectives
Through this page you will see some highlighted scattering examples and how to use them.
However, for all information about replicator camera use consult the API documentation .
Scattering objects in a surface
In this example we show you how to scatter objects in a 2D surface using the function randomizer.scatter_2d().
import omni.graph.core as og
import omni.replicator.core as rep
# create a plane to sample on
plane_samp = rep.create.plane(scale=4, rotation=(20, 0, 0))
def randomize_spheres():
# create small spheres to sample inside the plane
spheres = rep.create.sphere(scale=0.4, count=30)
# randomize
with spheres:
rep.randomizer.scatter_2d(plane_samp)
# Add color to small spheres
rep.randomizer.color(colors=rep.distribution.uniform((0.2, 0.2, 0.2), (1, 1, 1)))
return spheres.node
rep.randomizer.register(randomize_spheres)
with rep.trigger.on_frame(num_frames=10):
rep.randomizer.randomize_spheres()
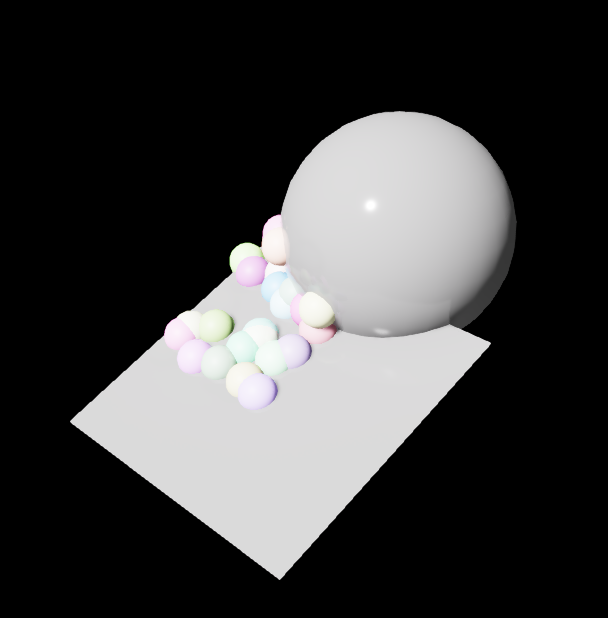
The spheres are scattered on the plane, but you should notice that they will intersect with each other.
Scatter 2D with collisions
Altering the code above, we can add check_for_collisions=True to ensure that none of the spheres overlap.
import omni.graph.core as og
import omni.replicator.core as rep
# create a plane to sample on
plane_samp = rep.create.plane(scale=4, rotation=(20, 0, 0))
def randomize_spheres():
# create small spheres to sample inside the plane
spheres = rep.create.sphere(scale=0.4, count=30)
# randomize
with spheres:
rep.randomizer.scatter_2d(plane_samp, check_for_collisions=True)
# Add color to small spheres
rep.randomizer.color(colors=rep.distribution.uniform((0.2, 0.2, 0.2), (1, 1, 1)))
return spheres.node
rep.randomizer.register(randomize_spheres)
with rep.trigger.on_frame(num_frames=10):
rep.randomizer.randomize_spheres()
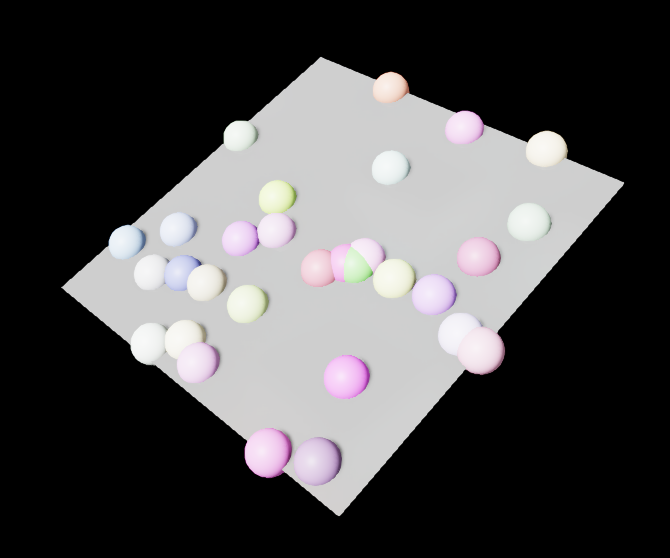
The spheres are now scattered without intersecting with each other.
Note
An error will be raised if no collision solution can be found within a reasonable amount of time (for instance: having too many objects)
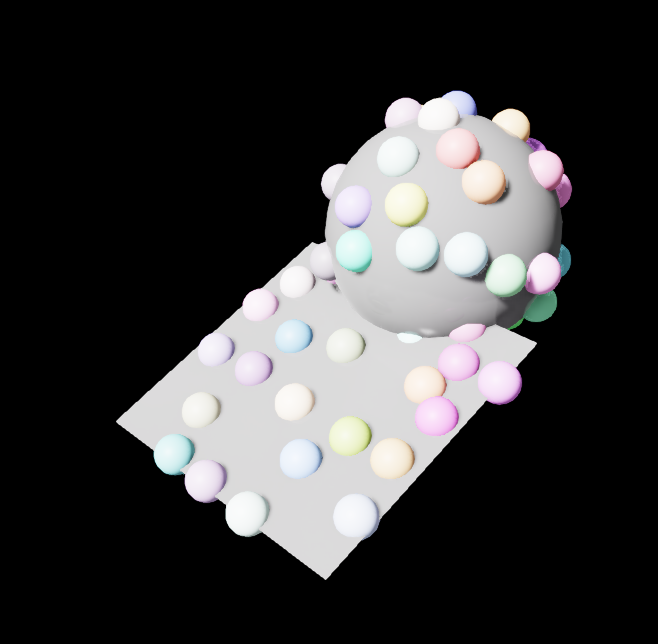
Multi-Surface Scatter 2D
In this example, the Scatter 2D node can be used for sampling on multiple surfaces.
We create a second surface, a large sphere, and sample 40 small spheres distributed across both surfaces.
import omni.replicator.core as rep
# A light to see
distance_light = rep.create.light(rotation=(-45, 0, 0), light_type="distant")
# Create a plane to sample on
plane_samp = rep.create.plane(scale=3, rotation=(20, 0, 0))
# Create a larger sphere to sample on the surface of
sphere_samp = rep.create.sphere(scale=2.4, position=(0, 100, -180))
def randomize_spheres():
# create small spheres to sample inside the plane
spheres = rep.create.sphere(scale=0.4, count=40)
# scatter small spheres
with spheres:
rep.randomizer.scatter_2d(surface_prims=[plane_samp, sphere_samp], check_for_collisions=True)
# Add color to small spheres
rep.randomizer.color(colors=rep.distribution.uniform((0.2, 0.2, 0.2), (1, 1, 1)))
return spheres.node
rep.randomizer.register(randomize_spheres)
with rep.trigger.on_frame(num_frames=10):
rep.randomizer.randomize_spheres()
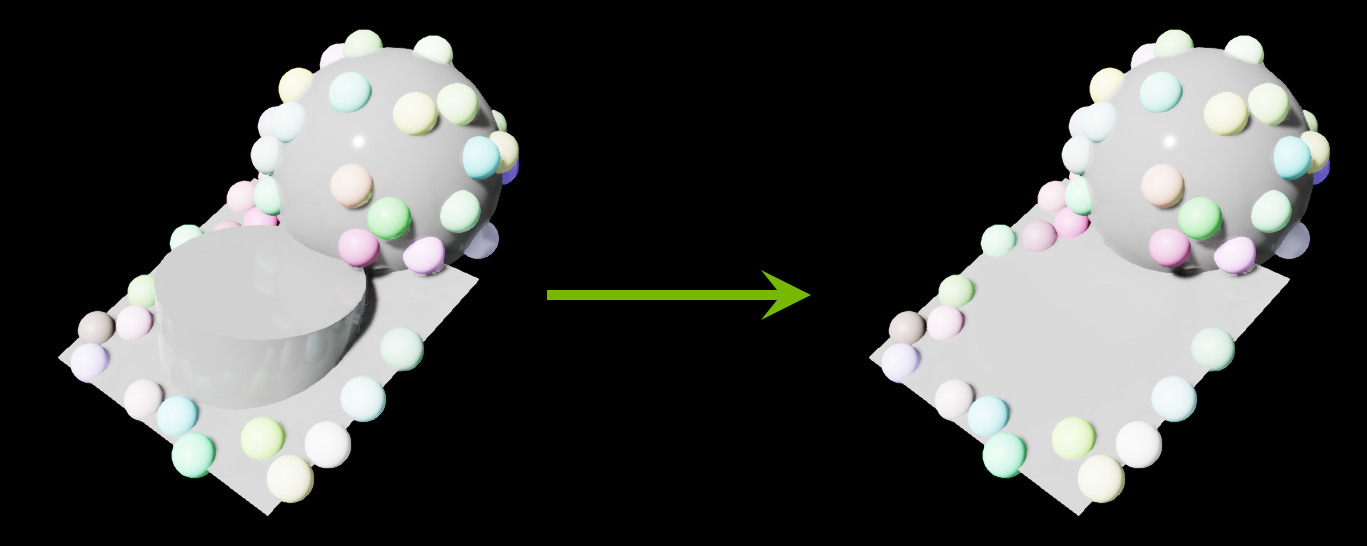
Scatter 2D avoiding objects
In this example we show the Scatter 2D node can allow for collision checking with other prims besides the ones created for sampling.
We create a large cylinder and check for collisions by adding it to the parameter list no_coll_prims.
The scattered spheres will now avoid placement where the cylinder is located. Multiple extra prims can be added for collision checking with this parameter.
import omni.replicator.core as rep
# A light to see
distance_light = rep.create.light(rotation=(-45, 0, 0), light_type="distant")
# Create a plane to sample on
plane_samp = rep.create.plane(scale=3, rotation=(20, 0, 0))
# Create a larger sphere to sample on the surface of
sphere_samp = rep.create.sphere(scale=2.4, position=(0, 100, -180))
# Create a larger cylinder we do not want to collide with
cylinder = rep.create.cylinder(
semantics=[("class", "cylinder")], scale=(2, 1, 2))
def randomize_spheres():
# create small spheres to sample inside the plane
spheres = rep.create.sphere(scale=0.4, count=60)
# scatter small spheres
with spheres:
rep.randomizer.scatter_2d(
surface_prims=[plane_samp, sphere_samp], no_coll_prims=[cylinder], check_for_collisions=True
)
# Add color to small spheres
rep.randomizer.color(colors=rep.distribution.uniform((0.2, 0.2, 0.2), (1, 1, 1)))
return spheres.node
rep.randomizer.register(randomize_spheres)
with rep.trigger.on_frame(num_frames=10):
rep.randomizer.randomize_spheres()
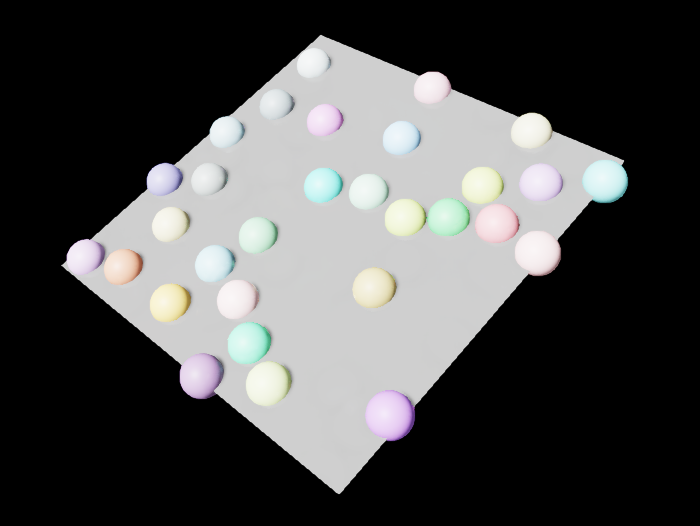
Scatter 2D with limits
In this example, we show that the Scatter 2D node can take in extra parameters for the min_samp and max_samp sampling bounds.
For example, you might want to stop sampling for everything beyond a certain value, i.e. y > 100.
To do this, specify min_samp=(X, Y, Z) and/or max_samp=(X, Y, Z) in the Scatter 2D node parameters.
The X,Y,Z values are all in world-space units.
import omni.replicator.core as rep
# A light to see
distance_light = rep.create.light(rotation=(-45, 0, 0), light_type="distant")
# Create a plane to sample on
plane_samp = rep.create.plane(scale=3, rotation=(20, 0, 0))
# Create a larger sphere to sample on the surface of
sphere_samp = rep.create.sphere(scale=2.4, position=(0, 100, -180))
def randomize_spheres():
# create small spheres to sample inside the plane
spheres = rep.create.sphere(scale=0.4, count=60)
# scatter small spheres
with spheres:
rep.randomizer.scatter_2d(
[plane_samp, sphere_samp],
min_samp=(None, None, None),
# Small spheres will not go beyond 0 in X, 110 in Y, 30 in Z world space
max_samp=(0, 110, 30),
check_for_collisions=False,
)
rep.randomizer.color(colors=rep.distribution.uniform((0.2, 0.2, 0.2), (1, 1, 1)))
return spheres.node
rep.randomizer.register(randomize_spheres)
with rep.trigger.on_frame(num_frames=10):
rep.randomizer.randomize_spheres()