Fields and Sliders#
Common Styling for Fields and Sliders#
Here is a list of common style you can customize on Fields and Sliders:
background_color (color): the background color of the field or slider
border_color (color): the border color if the field or slider background has a border
border_radius (float): the border radius if the user wants to round the field or slider
border_width (float): the border width if the field or slider background has a border
padding (float): the distance between the text and the border of the field or slider
font_size (float): the size of the text in the field or slider
Field#
There are fields for string, float and int models.
Except the common style for Fields and Sliders, here is a list of styles you can customize on Field:
color (color): the color of the text
background_selected_color (color): the background color of the selected text
StringField#
The StringField widget is a one-line text editor. A field allows the user to enter and edit a single line of plain text. It’s implemented using the model-delegate-view pattern and uses AbstractValueModel as the central component of the system.
The following example demonstrates how to connect a StringField and a Label. You can type anything into the StringField.

from omni.ui import color as cl
field_style = {
"Field": {
"background_color": cl(0.8),
"border_color": cl.blue,
"background_selected_color": cl.yellow,
"border_radius": 5,
"border_width": 1,
"color": cl.red,
"font_size": 20.0,
"padding": 5,
},
"Field:pressed": {"background_color": cl.white, "border_color": cl.green, "border_width": 2, "padding": 8},
}
def setText(label, text):
"""Sets text on the label"""
# This function exists because lambda cannot contain assignment
label.text = f"You wrote '{text}'"
with ui.HStack():
field = ui.StringField(style=field_style)
ui.Spacer(width=5)
label = ui.Label("", name="text")
field.model.add_value_changed_fn(lambda m, label=label: setText(label, m.get_value_as_string()))
ui.Spacer(width=10)
The following example demonstrates that the CheckBox’s model decides the content of the Field. Click to edit and update the string field value also updates the value of the CheckBox. The field can only have one of the two options, either ‘True’ or ‘False’, because the model only supports those two possibilities.

from omni.ui import color as cl
with ui.HStack():
field = ui.StringField(width=100, style={"background_color": cl.black})
checkbox = ui.CheckBox(width=0)
field.model = checkbox.model
In this example, the field can have anything because the model accepts any string. The model returns bool for checkbox, and the checkbox is unchecked when the string is empty or ‘False’.

from omni.ui import color as cl
with ui.HStack():
field = ui.StringField(width=100, style={"background_color": cl.black})
checkbox = ui.CheckBox(width=0)
checkbox.model = field.model
The Field widget doesn’t keep the data due to the model-delegate-view pattern. However, there are two ways to track the state of the widget. It’s possible to re-implement the AbstractValueModel. The second way is using the callbacks of the model. Here is a minimal example of callbacks. When you start editing the field, you will see “Editing is started”, and when you finish editing by press enter, you will see “Editing is finished”.

def on_value(label):
label.text = "Value is changed"
def on_begin(label):
label.text = "Editing is started"
def on_end(label):
label.text = "Editing is finished"
label = ui.Label("Nothing happened", name="text")
model = ui.StringField().model
model.add_value_changed_fn(lambda m, l=label: on_value(l))
model.add_begin_edit_fn(lambda m, l=label: on_begin(l))
model.add_end_edit_fn(lambda m, l=label: on_end(l))
Multiline StringField#
Property multiline of StringField allows users to press enter and create a new line. It’s possible to finish editing with Ctrl-Enter.

from omni.ui import color as cl
import inspect
field_style = {
"Field": {
"background_color": cl(0.8),
"color": cl.black,
},
"Field:pressed": {"background_color": cl(0.8)},
}
field_callbacks = lambda: field_callbacks()
with ui.Frame(style=field_style, height=200):
model = ui.SimpleStringModel("hello \nworld \n")
field = ui.StringField(model, multiline=True)
FloatField and IntField#
The following example shows how string field, float field and int field interact with each other. All three fields share the same default FloatModel:
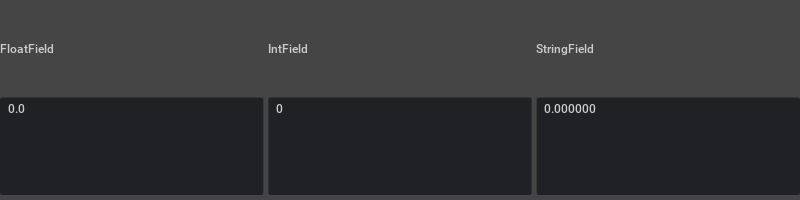
with ui.HStack(spacing=5):
ui.Label("FloatField")
ui.Label("IntField")
ui.Label("StringField")
with ui.HStack(spacing=5):
left = ui.FloatField()
center = ui.IntField()
right = ui.StringField()
center.model = left.model
right.model = left.model
ui.Spacer(height=5)
MultiField#
MultiField widget groups the widgets that have multiple similar widgets to represent each item in the model. It’s handy to use them for arrays and multi-component data like float3, matrix, and color.
MultiField is using Field as the Type Selector. Therefore, the list of styless we can customize on MultiField is the same as Field
MultiIntField#
Each of the field value could be changed by editing
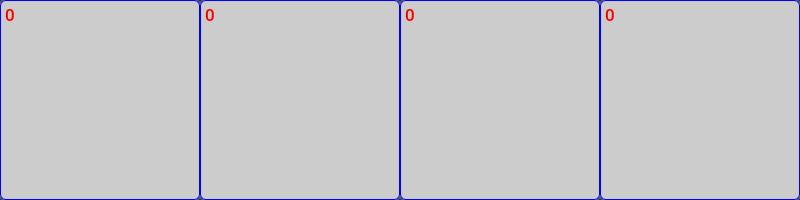
from omni.ui import color as cl
field_style = {
"Field": {
"background_color": cl(0.8),
"border_color": cl.blue,
"border_radius": 5,
"border_width": 1,
"color": cl.red,
"font_size": 20.0,
"padding": 5,
},
"Field:pressed": {"background_color": cl.white, "border_color": cl.green, "border_width": 2, "padding": 8},
}
ui.MultiIntField(0, 0, 0, 0, style=field_style)
MultiFloatField#
Use MultiFloatField to construct a matrix field:
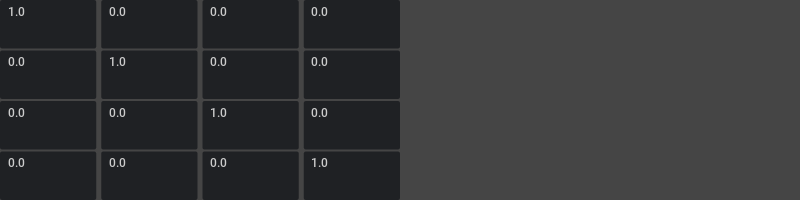
args = [1.0 if i % 5 == 0 else 0.0 for i in range(16)]
ui.MultiFloatField(*args, width=ui.Percent(50), h_spacing=5, v_spacing=2)
MultiFloatDragField#
Each of the field value could be changed by dragging
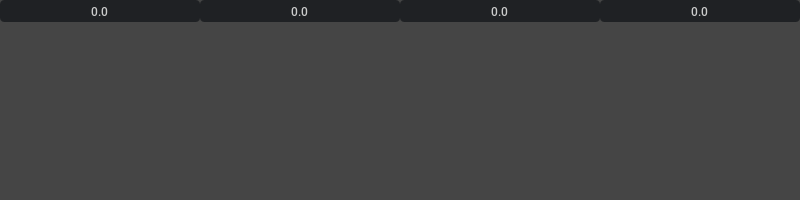
ui.MultiFloatDragField(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
Sliders#
The Sliders are more like a traditional slider that can be dragged and snapped where you click. The value of the slider can be shown on the slider or not, but can not be edited directly by clicking.
Except the common style for Fields and Sliders, here is a list of styles you can customize on ProgressBar:
color (color): the color of the text
secondary_color (color): the color of the handle in
ui.SliderDrawMode.HANDLEdraw_mode or the background color of the left portion of the slider inui.SliderDrawMode.DRAGdraw_mode
secondary_selected_color (color): the color of the handle when selected, not useful when the draw_mode is FILLED since there is no handle drawn.
draw_mode (enum): defines how the slider handle is drawn. There are three types of draw_mode.
ui.SliderDrawMode.HANDLE: draw the handle as a knob at the slider position
ui.SliderDrawMode.DRAG: the same as
ui.SliderDrawMode.HANDLEfor nowui.SliderDrawMode.FILLED: the handle is eventually the boundary between the
secondary_colorandbackground_color
Sliders with different draw_mode:

from omni.ui import color as cl
with ui.VStack(spacing=5):
ui.FloatSlider(style={"background_color": cl(0.8),
"secondary_color": cl(0.6),
"color": cl(0.1),
"draw_mode": ui.SliderDrawMode.HANDLE}
).model.set_value(0.5)
ui.FloatSlider(style={"background_color": cl(0.8),
"secondary_color": cl(0.6),
"color": cl(0.1),
"draw_mode": ui.SliderDrawMode.DRAG}
).model.set_value(0.5)
ui.FloatSlider(style={"background_color": cl(0.8),
"secondary_color": cl(0.6),
"color": cl(0.1),
"draw_mode": ui.SliderDrawMode.FILLED}
).model.set_value(0.5)
FloatSlider#
Default slider whose range is between 0 to 1:
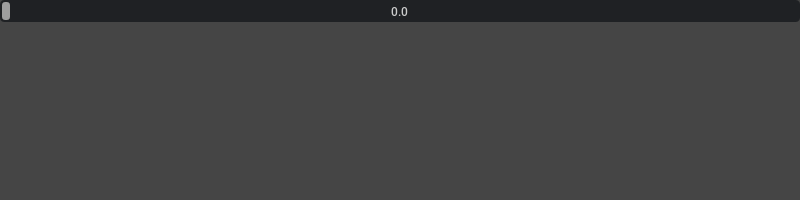
ui.FloatSlider()
With defined Min/Max whose range is between min to max:
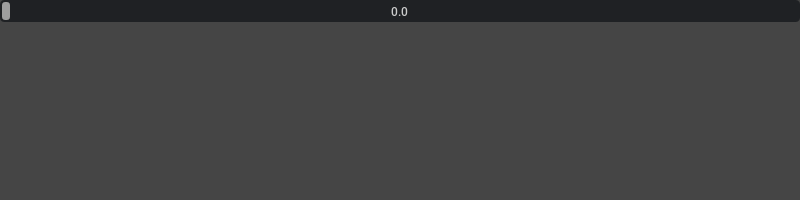
ui.FloatSlider(min=0, max=10)
With defined Min/Max from the model. Notice the model allows the value range between 0 to 100, but the FloatSlider has a more strict range between 0 to 10.
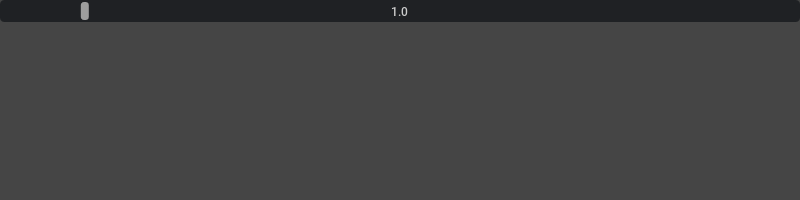
model = ui.SimpleFloatModel(1.0, min=0, max=100)
ui.FloatSlider(model, min=0, max=10)
With styles and rounded slider:

from omni.ui import color as cl
with ui.HStack(width=200):
ui.Spacer(width=20)
with ui.VStack():
ui.Spacer(height=5)
ui.FloatSlider(
min=-180,
max=180,
style={
"color": cl.blue,
"background_color": cl(0.8),
"draw_mode": ui.SliderDrawMode.HANDLE,
"secondary_color": cl.red,
"secondary_selected_color": cl.green,
"font_size": 20,
"border_width": 3,
"border_color": cl.black,
"border_radius": 10,
"padding": 10,
}
)
ui.Spacer(height=5)
ui.Spacer(width=20)
Filled mode slider with style:

from omni.ui import color as cl
with ui.HStack(width=200):
ui.Spacer(width=20)
with ui.VStack():
ui.Spacer(height=5)
ui.FloatSlider(
min=-180,
max=180,
style={
"color": cl.blue,
"background_color": cl(0.8),
"draw_mode": ui.SliderDrawMode.FILLED,
"secondary_color": cl.red,
"font_size": 20,
"border_radius": 10,
"padding": 10,
}
)
ui.Spacer(height=5)
ui.Spacer(width=20)
Transparent background:

from omni.ui import color as cl
with ui.HStack(width=200):
ui.Spacer(width=20)
with ui.VStack():
ui.Spacer(height=5)
ui.FloatSlider(
min=-180,
max=180,
style={
"draw_mode": ui.SliderDrawMode.HANDLE,
"background_color": cl.transparent,
"color": cl.red,
"border_width": 1,
"border_color": cl.white,
}
)
ui.Spacer(height=5)
ui.Spacer(width=20)
Slider with transparent value. Notice the use of step attribute
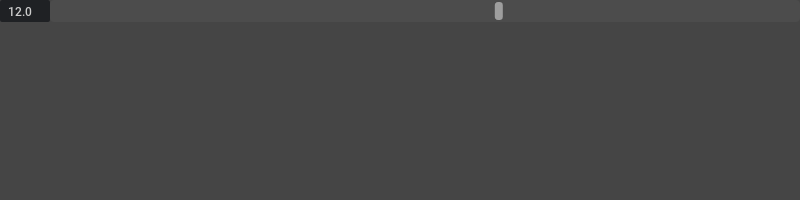
from omni.ui import color as cl
with ui.HStack():
# a separate float field
field = ui.FloatField(height=15, width=50)
# a slider using field's model
ui.FloatSlider(
min=0,
max=20,
step=0.25,
model=field.model,
style={
"color":cl.transparent,
"background_color": cl(0.3),
"draw_mode": ui.SliderDrawMode.HANDLE}
)
# default value
field.model.set_value(12.0)
IntSlider#
Default slider whose range is between 0 to 100:
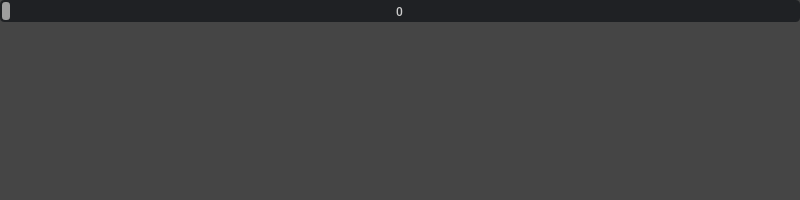
ui.IntSlider()
With defined Min/Max whose range is between min to max. Note that the handle width is much wider.
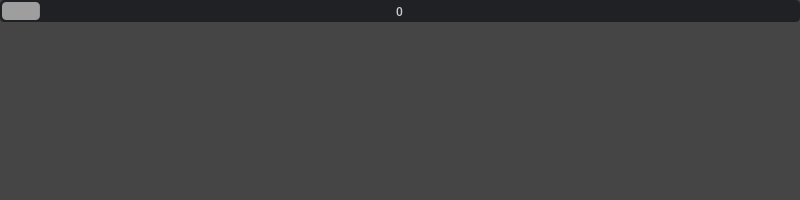
ui.IntSlider(min=0, max=20)
With style:

from omni.ui import color as cl
with ui.HStack(width=200):
ui.Spacer(width=20)
with ui.VStack():
ui.Spacer(height=5)
ui.IntSlider(
min=0,
max=20,
style={
"background_color": cl("#BBFFBB"),
"color": cl.purple,
"draw_mode": ui.SliderDrawMode.HANDLE,
"secondary_color": cl.green,
"secondary_selected_color": cl.red,
"font_size": 14.0,
"border_width": 3,
"border_color": cl.green,
"padding": 5,
}
).model.set_value(4)
ui.Spacer(height=5)
ui.Spacer(width=20)
Drags#
The Drags are very similar to Sliders, but more like Field in the way that they behave. You can double click to edit the value but they also have a mean to be ‘Dragged’ to increase or decrease the value.
Except the common style for Fields and Sliders, here is a list of styles you can customize on ProgressBar:
color (color): the color of the text
secondary_color (color): the left portion of the slider in
ui.SliderDrawMode.DRAGdraw_mode
FloatDrag#
Default float drag whose range is -inf and +inf
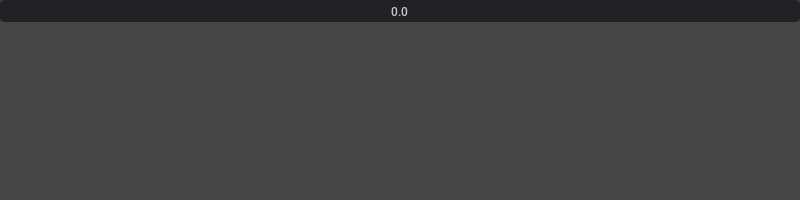
ui.FloatDrag()
With defined Min/Max whose range is between min to max:
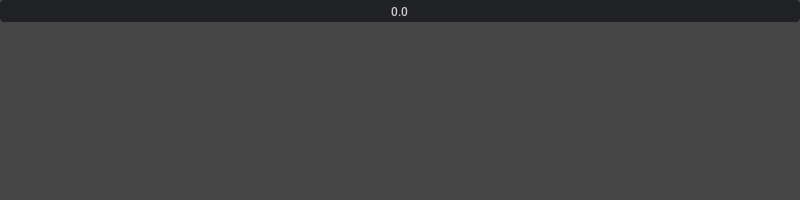
ui.FloatDrag(min=-10, max=10, step=0.1)
With styles and rounded shape:

from omni.ui import color as cl
with ui.HStack(width=200):
ui.Spacer(width=20)
with ui.VStack():
ui.Spacer(height=5)
ui.FloatDrag(
min=-180,
max=180,
style={
"color": cl.blue,
"background_color": cl(0.8),
"secondary_color": cl.red,
"font_size": 20,
"border_width": 3,
"border_color": cl.black,
"border_radius": 10,
"padding": 10,
}
)
ui.Spacer(height=5)
ui.Spacer(width=20)
IntDrag#
Default int drag whose range is -inf and +inf
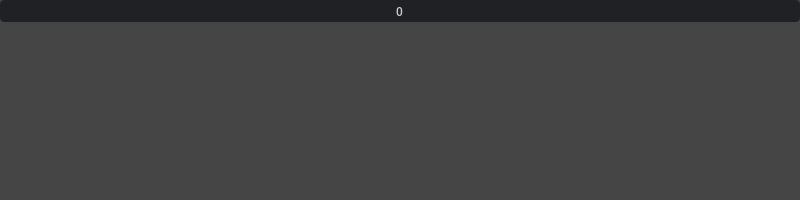
ui.IntDrag()
With defined Min/Max whose range is between min to max:
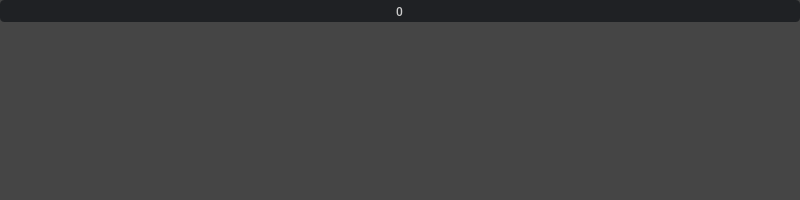
ui.IntDrag(min=-10, max=10)
With styles and rounded slider:

from omni.ui import color as cl
with ui.HStack(width=200):
ui.Spacer(width=20)
with ui.VStack():
ui.Spacer(height=5)
ui.IntDrag(
min=-180,
max=180,
style={
"color": cl.blue,
"background_color": cl(0.8),
"secondary_color": cl.purple,
"font_size": 20,
"border_width": 4,
"border_color": cl.black,
"border_radius": 20,
"padding": 5,
}
)
ui.Spacer(height=5)
ui.Spacer(width=20)
ProgressBar#
A ProgressBar is a widget that indicates the progress of an operation.
Except the common style for Fields and Sliders, here is a list of styles you can customize on ProgressBar:
color (color): the color of the progress bar indicating the progress value of the progress bar in the portion of the overall value
secondary_color (color): the color of the text indicating the progress value
In the following example, it shows how to use ProgressBar and override the style of the overlay text.

from omni.ui import color as cl
class CustomProgressValueModel(ui.AbstractValueModel):
"""An example of custom float model that can be used for progress bar"""
def __init__(self, value: float):
super().__init__()
self._value = value
def set_value(self, value):
"""Reimplemented set"""
try:
value = float(value)
except ValueError:
value = None
if value != self._value:
# Tell the widget that the model is changed
self._value = value
self._value_changed()
def get_value_as_float(self):
return self._value
def get_value_as_string(self):
return "Custom Overlay"
with ui.VStack(spacing=5):
# Create ProgressBar
first = ui.ProgressBar()
# Range is [0.0, 1.0]
first.model.set_value(0.5)
second = ui.ProgressBar()
second.model.set_value(1.0)
# Overrides the overlay of ProgressBar
model = CustomProgressValueModel(0.8)
third = ui.ProgressBar(model)
third.model.set_value(0.1)
# Styling its color
fourth = ui.ProgressBar(style={"color": cl("#0000dd")})
fourth.model.set_value(0.3)
# Styling its border width
ui.ProgressBar(style={"border_width": 2, "border_color": cl("#dd0000"), "color": cl("#0000dd")}).model.set_value(0.7)
# Styling its border radius
ui.ProgressBar(style={"border_radius": 100, "color": cl("#0000dd")}).model.set_value(0.6)
# Styling its background color
ui.ProgressBar(style={"border_radius": 10, "background_color": cl("#0000dd")}).model.set_value(0.6)
# Styling the text color
ui.ProgressBar(style={"ProgressBar":{"border_radius": 30, "secondary_color": cl("#00dddd"), "font_size": 20}}).model.set_value(0.6)
# Two progress bars in a row with padding
with ui.HStack():
ui.ProgressBar(style={"color": cl("#0000dd"), "padding": 100}).model.set_value(1.0)
ui.ProgressBar().model.set_value(0.0)
Tooltip#
All Widget can be augmented with a tooltip. It can take 2 forms, either a simple ui.Label or a callback when using the callback of tooltip_fn= or widget.set_tooltip_fn(). You can create the tooltip for any widget.
Except the common style for Fields and Sliders, here is a list of styles you can customize on Line:
color (color): the color of the text of the tooltip.
margin_width (float): the width distance between the tooltip content and the parent widget defined boundary
margin_height (float): the height distance between the tooltip content and the parent widget defined boundary
Here is a simple label tooltip with style when you hover over a button:

from omni.ui import color as cl
tooltip_style = {
"Tooltip": {
"background_color": cl("#DDDD00"),
"color": cl(0.2),
"padding": 10,
"border_width": 3,
"border_color": cl.red,
"font_size": 20,
"border_radius": 10}}
ui.Button("Simple Label Tooltip", name="tooltip", width=200, tooltip="I am a text ToolTip", style=tooltip_style)
You can create a callback function as the tooltip where you can create any types of widgets you like in the tooltip and layout them. Make the tooltip very illustrative to have Image or Field or Label etc.

from omni.ui import color as cl
def create_tooltip():
with ui.VStack(width=200, style=tooltip_style):
with ui.HStack():
ui.Label("Fancy tooltip", width=150)
ui.IntField().model.set_value(12)
ui.Line(height=2, style={"color":cl.white})
with ui.HStack():
ui.Label("Anything is possible", width=150)
ui.StringField().model.set_value("you bet")
image_source = "resources/desktop-icons/omniverse_512.png"
ui.Image(
image_source,
width=200,
height=200,
alignment=ui.Alignment.CENTER,
style={"margin": 0},
)
tooltip_style = {
"Tooltip": {
"background_color": cl(0.2),
"border_width": 2,
"border_radius": 5,
"margin_width": 5,
"margin_height": 10
},
}
ui.Button("Callback function Tooltip", width=200, style=tooltip_style, tooltip_fn=create_tooltip)
You can define a fixed position for tooltip:

ui.Button("Fixed-position Tooltip", width=200, tooltip="Hello World", tooltip_offset_y=22)
You can also define a random position for tooltip:

import random
button = ui.Button("Random-position Tooltip", width=200, tooltip_offset_y=22)
def create_tooltip(button=button):
button.tooltip_offset_x = random.randint(0, 200)
ui.Label("Hello World")
button.set_tooltip_fn(create_tooltip)